커뮤니티
부경투데이
- 국립 부경대학교의 다양한 모습과 소식을 접하시면 부경대학교가 한번 더 가까워집니다.
| 빛 이용 암 치료 나노소재 연구 '주목' (Light-Activated Nanomaterials for Cancer Treatment ‘Draw Attention’) | |||
| 작성자 | 대외홍보센터 | 작성일 | 2025-09-05 |
| 조회수 | 985 | ||
| 빛 이용 암 치료 나노소재 연구 '주목' (Light-Activated Nanomaterials for Cancer Treatment ‘Draw Attention’) | |||||
 |
대외홍보센터 |  |
2025-09-05 | 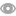 |
985 |
국립부경대 연구, 세계 상위 0.12% 국제학술지에 실렸다
- 빛 이용 암 치료를 위한 나노소재 연구 … <Coordination Chemistry Reviews> 게재

△ 왼쪽부터 응우옌 티 수언 석사과정생, 안재성 교수, 수딥 몬달 교수, 오정환 교수.
국립부경대학교(총장 배상훈) 연구팀의 레이저를 이용한 암 진단과 치료를 위한 생체모방 나노소재 플랫폼 연구에 대한 최신 동향 논문이 화학 분야 세계적 권위의 국제학술지 엘스비어(Elsevier)의 <Coordination Chemistry Reviews>(IF: 23.5, JCR 상위 0.12%)에 실렸다.
논문 제목은 ‘Functional Nanostructured Biomaterials in Cancer Phototherapy and Biomedicine’이다. 이 논문은 생체 구조와 기능을 모방한 혁신적 나노 플랫폼이 레이저 기반 광열치료(PTT)와 광역동치료(PDT)의 실제 임상에 적용하는 데 정확성과 안전성을 어떻게 향상하는지 규명했다.
오정환 교수(의공학전공), 수딥 몬달 교수(디지털헬스케어연구센터), 안재성 교수(RLRC 센터), 응우옌 티 수언 대학원생(4차산업융합바이오닉스공학과) 등 공동연구팀이 본 연구를 함께 수행했다.
연구팀은 이번 연구에서 나노 플랫폼의 설계 원리, 기능화 전략, 의학적 응용에 중점을 두고 유기, 무기, 고분자 기반 나노소재의 발전상을 정리하였으며, 이와 함께 실제 환자 임상 적용 시 생체적합성, 표적 효율성, 분해 조절 능력을 높여 기존 나노의학의 주요 한계였던 세포 독성 및 낮은 표적 특이성을 극복하는 과정을 규명했다.
이 논문은 레이저를 이용한 진단과 치료 응용을 위한 차세대 나노 광민감제 설계 전략을 제시함으로써 미래의 정밀의학과 스마트 헬스케어 분야의 발전을 위한 중요한 통찰을 제공한다는 평가를 받고 있다.
이번 연구는 한국연구재단(NRF) 지역혁신 선도연구센터의 지원을 받아 수행되었으며, 나노소재 기반 광의학 분야의 학문적 가치와 발전 가능성을 입증함에 따라, 향후 암 치료용 광치료제 및 진단용 나노소재 개발에 크게 이바지할 것으로 기대된다. <부경투데이>
Pukyong National University Research Published in Top 0.12% Global Journal
- Light-Activated Nanomaterials for Cancer Therapy Featured in <Coordination Chemistry Reviews>
A research team from Pukyong National University (President Bae Sang-Hoon) has published a review article on biomimetic nanomaterial platforms for laser-based cancer diagnosis and therapy in <Coordination Chemistry Reviews>, a globally renowned journal in the field of chemistry published by Elsevier (Impact Factor: 23.5, JCR top 0.12%).
The article, titled ‘Functional Nanostructured Biomaterials in Cancer Phototherapy and Biomedicine’ explores how innovative nanoplatforms that mimic biological structures and functions enhance the precision and safety of laser-driven photothermal therapy (PTT) and photodynamic therapy (PDT) for real-world clinical applications.
The research was jointly conducted by Professor Oh Jung-Hwan (Department of Biomedical Engineering), Professor Sudip Mondal (Digital Healthcare Research Center), Professor An Jae-Seong (RLRC Center), and graduate student Nguyen Thi Xuan (Department of Bionics Engineering for the Fourth Industrial Revolution Convergence).
In this study, the team focused on the design principles, functionalization strategies, and biomedical applications of nanoplatforms, presenting the development trends of organic, inorganic, and polymer-based nanomaterials. Furthermore, they outlined how these platforms enhance biocompatibility, target efficiency, and degradation control―key to overcoming the major limitations of traditional nanomedicine, such as cytotoxicity and low target specificity, when applied in real patient clinical settings.
The paper has been recognized for offering critical insights into the future of precision medicine and smart healthcare by proposing next-generation design strategies for nano photosensitizers applied in laser-based diagnosis and treatment.
This research was supported by the Regional Leading Research Center (RLRC) program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). By demonstrating the academic value and development potential of nanomaterial-based photomedicine, the study is expected to make significant contributions to the future development of photosensitizers for cancer treatment and diagnostic nanomaterials. <Pukyong Today>