연구/산학
PKNU Research 1000
| PKNU & SNU & Cambridge & Oxford | |||
| 작성자 | 대외협력과 | 작성일 | 2023-03-23 |
| 조회수 | 744 | ||
| PKNU & SNU & Cambridge & Oxford | |||||
 |
대외협력과 |  |
2023-03-23 |  |
744 |
A review article by research team with prof. Lee Bo-Ram from PKNU appeared on the cover of <Joule>, an international science journal
- research on development strategies for performance improvement of next-generation display ‘Perovskite LEDs’

△ The cover of <Joule>, dated February 15th, featuring an image from a review article by prof. Lee Bo-Ram’s team.
Professor Lee Bo-Ram (Dept. of physics) and her research team from Pukyong National University published a review article on the cover of <Joule>(IF=46.048), an international science journal, drawing attention from the academic world.
<Joule> is a journal in the energy field with the highest citation index (IF) among the sister journals of <Cell>, known as one of the world's top three journals along with <Nature> and <Science>.
The cover of this journal, dated February 15th, was covered by the research team of professor Lee Bo-Ram’s review article, ‘Passivation strategies for mitigating defect challenges in halide perovskite light-emitting diodes’.
The research team is made up with great scholars such as professor Lee Bo-Ram and dr. Xinyu Shen from Pukyong National University, professor Kang Kee-Hoon from Seoul National University, professors Richard H. Friend and Samuele D. Stranks from university of Cambridge in England, and professor Henry J. Snaith from university of Oxford.
In this paper, the research team presents problems and solutions to be overcome in current research on perovskite LEDs, and promotes research on the development of perovskite LEDs that maintain high efficiency and high stability. Especially, various previously reported defect passivation strategies are systematically reviewed, summarized, and presented through four basic principles (ionic bonding, coordinate covalent bonding, hydrogen bonding, and core-shell structure) and their synergistic multiple combinations.
Metal halide perovskite (MHP) is a material with great potential for next-generation display applications due to its high color purity and high photoluminescence quantum yield.
Perovskite materials are known to have higher defect tolerance than conventional semiconductor materials, but in fact, various defects occur in the process of thinning perovskite materials. In addition, defects occur on multilayer between the electron transport layer and the perovskite material, which limits the device performance of LEDs.
To prevent device performance degradation, many researchers have continuously improved the performance of perovskite LEDs through various defect passivation strategies, and currently, external quantum efficiencies of up to 28.9%, which are close to commercialization, have been reported.
Professor Lee Bo-Ram said, “We expect that the results of this paper will serve as a reference for industry and academia to discover the greater potential of perovskite for photoelectronic devices.”
As for the research, it was carried out with support from the Ministry of science and ICT (MSIT) and the National research foundation's BrainLink project, nano and material technology development program, young researcher program, mid-career researcher program, and the key research institutes for universities support project.
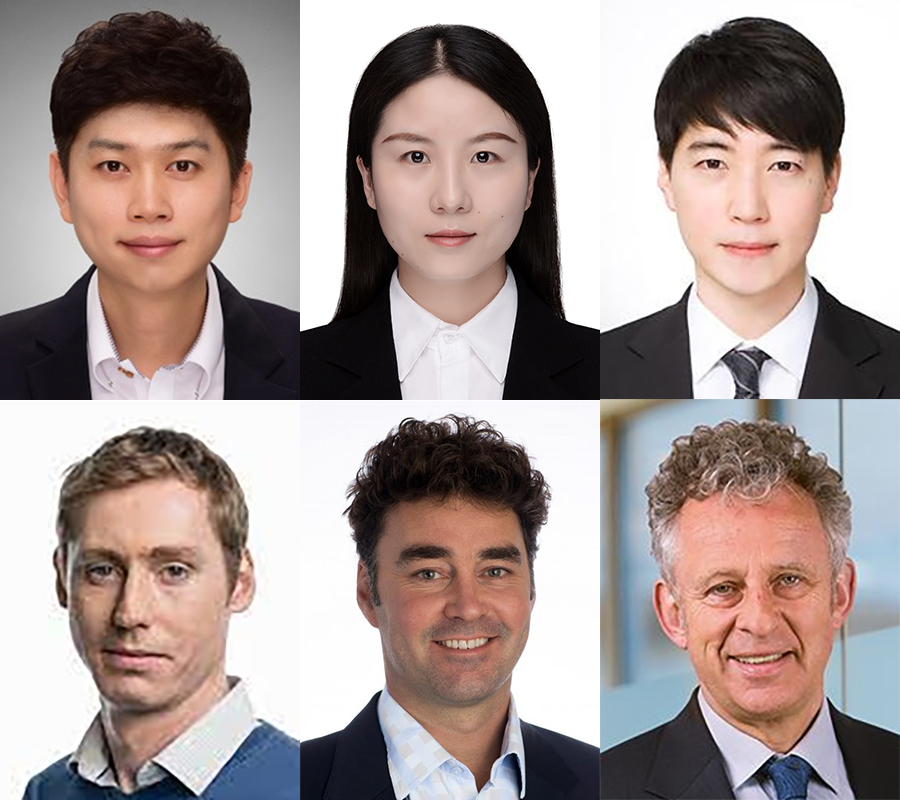

△ The research team. (from top left) prof. Lee Bo-Ram, dr. Xinyu Shen, prof. Kang Kee-Hoon, (from bottom left) prof. Samuele D. Stranks, prof. Henry J. Snaith, and prof. Richard H. Friend.