커뮤니티
부경투데이
- 국립 부경대학교의 다양한 모습과 소식을 접하시면 부경대학교가 한번 더 가까워집니다.
| '글로벌 기초연구실' 선정(Selected for Global Basic Research Laboratory Program) | |||
| 작성자 | 대외홍보센터 | 작성일 | 2025-06-04 |
| 조회수 | 1059 | ||
| '글로벌 기초연구실' 선정(Selected for Global Basic Research Laboratory Program) | |||||
 |
대외홍보센터 |  |
2025-06-04 | 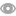 |
1059 |
국립부경대 박상혁 교수팀, ‘글로벌 기초연구실 지원사업’ 선정
- 첨단 오가노이드 실시간 분석 평가 플랫폼 개발 추진
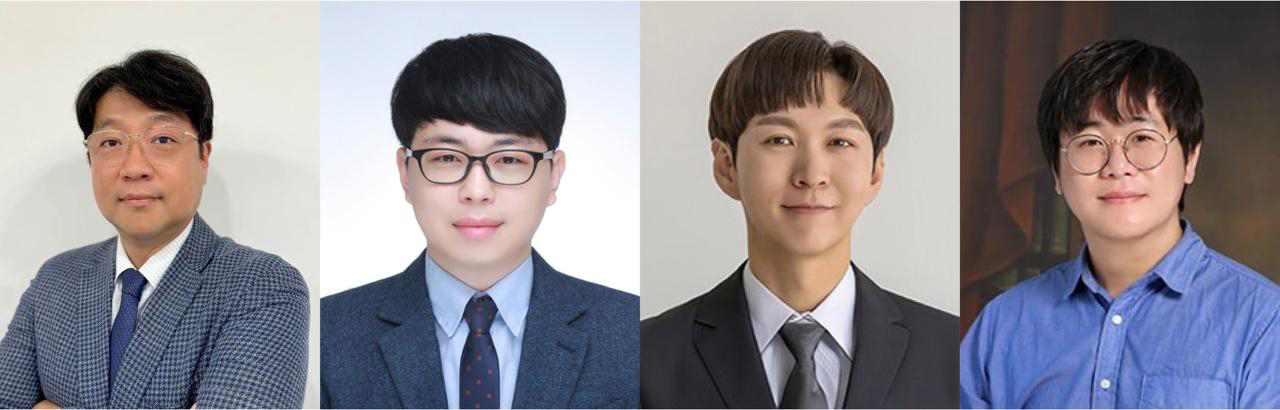

△ 왼쪽부터 박상혁, 남승윤, 엄우람, 윤창한 교수.
국립부경대학교(총장 배상훈)는 박상혁 교수(스마트헬스케어학부 의공학전공) 연구팀이 과학기술정보통신부와 한국연구재단의 ‘2025년도 글로벌 기초연구실(BRL) 지원 사업’에 선정됐다고 밝혔다.
박상혁 교수 연구팀은 공동 연구진인 남승윤(의공학전공), 엄우람(생물공학전공), 윤창한(인제대 의공학과) 교수와 함께 ‘첨단바이오 오가노이드 비파괴 특성 분석을 위한 AI 연계 SWE-ERS 통합 플랫폼 개발 글로벌 기초연구실’로 이번 사업에 최종 선정됐다.
글로벌 기초연구실 지원사업은 특정 연구주제 중심의 소규모 기초연구 그룹을 지원해 국가 기초연구 역량을 강화하기 위한 사업이다.
연구팀은 이번 선정으로 앞으로 3년간 15억 원을 지원받아 비파괴 방식 기반의 첨단 오가노이드의 실시간 분석을 위한 평가 플랫폼 개발에 나선다.
오가노이드는 조직 및 장기의 구조와 기능을 모방하는 3D 미니장기 혹은 장기 유사체를 의미하며, 맞춤 치료용 질환 모델링, 약물 스크리닝, 동물실험 대체 시험법, 조직재생 치료제로 활용할 수 있어 최근 주목받는 첨단 바이오소재다.
하지만 현재까지 형태가 일정하지 않은 비정형 오가노이드 인공조직에 대한 맞춤형 평가법이 없어, 주로 제작된 오가노이드를 파괴하는 방식으로 물리적, 화학적 분석이 수행되기 때문에 시간과 비용 소모가 크다는 한계가 있다. 또 대상 조직별 오가노이드 특성에 대한 객관적인 평가 기준이 없다는 제한점도 있다.
연구팀은 이 같은 문제를 극복하기 위해 생화학적 및 물리적 특성 변화를 비파괴적으로 측정하고, AI와 연계해 오가노이드의 분화도를 예측하는 기술 개발에 도전한다.
연구진은 집단 연구를 통해 3차원 오가노이드 배양 과정에서 배지로 방출되는 엑소좀(exosome) 내부에 존재하는 RNA 서열을 분석(ERS)해 비파괴적으로 오가노이드 조직 내의 성숙도를 확인하고, 2D 어레이 기반의 횡파 탄성초음파(SWE)를 활용해 오가노이드의 위치 및 시간별 기계적 특성 변화를 측정 분석하는 기술을 개발할 계획이다. 또 AI 기반 솔루션을 제공해 비파괴 분석법 간의 상관관계와 연계성 분석도 수행한다.
연구 책임을 맡은 박상혁 교수는 “본 연구는 첨단 재생의학 분야에서 오가노이드뿐만 아니라 이식형 생체소재 및 조직공학 장기 제작의 스케일업 공정에 필수적인 핵심 원천 기술을 개발하는 융합연구로, 학과 내 지역혁신 선도연구센터 및 중점연구소와의 연계를 통해 첨단 재생의공학 심화 연구의 선두 기초연구실이 될 수 있도록 노력하겠다.”라고 밝혔다. <부경투데이>
Professor Park Sang-hyuk’s Team at Pukyong National University, Selected for ‘Global Research Laboratory Program’
- Project to Develop Advanced Real-Time Organoid Analysis and Evaluation Platform
Pukyong National University (President Bae Sang-hoon) announced that a research team led by Professor Park Sang-hyuk (Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Smart Healthcare) has been selected for the 2025 Global Basic Research Laboratory (BRL) Program, funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Professor Park Sang-hyuk’s team, in collaboration with Professors Nam Seung-yoon (Department Biomedical Engineering), Eom Woo-ram (Department of Biotechnology), and Yoon Chang-han (Department of Biomedical Engineering, Inje University), was selected for its proposal titled “Global Research Laboratory for the Development of an AI-Integrated SWE-ERS Platform for Non-Destructive Characterization of Advanced Bio-Organoids.”
The Global Basic Research Laboratory program supports small-scale research groups focused on specific topics, with the goal of strengthening the nation’s capacity for basic science research.
With this selection, the research team will receive 1.5 billion KRW in funding over the next three years to develop a real-time evaluation platform for advanced organoids using non-destructive analysis methods.
Organoids are three-dimensional mini-organs or organ-like structures that mimic the architecture and function of real tissues and organs. They are considered next-generation bio-materials with promising applications in personalized disease modeling, drug screening, alternatives to animal testing, and regenerative medicine.
However, current evaluation methods for irregularly shaped artificial organoid tissues are limited. Because there are no customized assessment tools, researchers often rely on destructive techniques that involve breaking down the organoids for physical and chemical analysis―an approach that is time-consuming and costly. In addition, the lack of standardized criteria for evaluating organoid characteristics across different tissue types remains a significant challenge.
To address these challenges, the research team aims to develop a non-destructive evaluation technology that measures biochemical and physical property changes in organoids and predicts their differentiation levels through artificial intelligence.
Through collaborative research, the team plans to analyze RNA sequences contained within exosomes released into the culture medium during the 3D organoid growth process―a method known as Exosome RNA Sequencing (ERS)―to non-destructively assess tissue maturity. In addition, they will develop a technique using shear wave elastography (SWE) based on a 2D array system to measure and analyze changes in the mechanical properties of organoids over time and location. The project also includes the development of AI-based solutions to analyze correlations and interrelationships between these non-invasive evaluation methods.
Professor Park Sang-hyuk, the principal investigator, stated, “This research represents a multidisciplinary effort to develop core technologies essential for scaling up implantable biomaterials and engineered organs in advanced regenerative medicine. We aim to establish this laboratory as a leading center for foundational research in regenerative biomedical engineering by closely collaborating with the university’s Regional Innovation Leading Research Center and other key research institutes.” <Pukyong Today>