커뮤니티
부경투데이
- 국립 부경대학교의 다양한 모습과 소식을 접하시면 부경대학교가 한번 더 가까워집니다.
| '항암효과↑' 스마트 약물 전달 시스템 개발(‘Anti-cancer effect ↑’ Development of Smart Drug Delivery System) | |||
| 작성자 | 대외홍보센터 | 작성일 | 2025-06-20 |
| 조회수 | 938 | ||
| '항암효과↑' 스마트 약물 전달 시스템 개발(‘Anti-cancer effect ↑’ Development of Smart Drug Delivery System) | |||||
 |
대외홍보센터 |  |
2025-06-20 |  |
938 |
국립부경대, 암세포에 항암제 전달 향상 ‘스마트 약물 전달 시스템’ 개발
- 김병국 박사수료생·임권택 교수·박상혁 교수 연구팀
- ‘산화-환원반응 가교 말토헵타오스 기반 마이셀’ 개발 … 국제학술지 게재
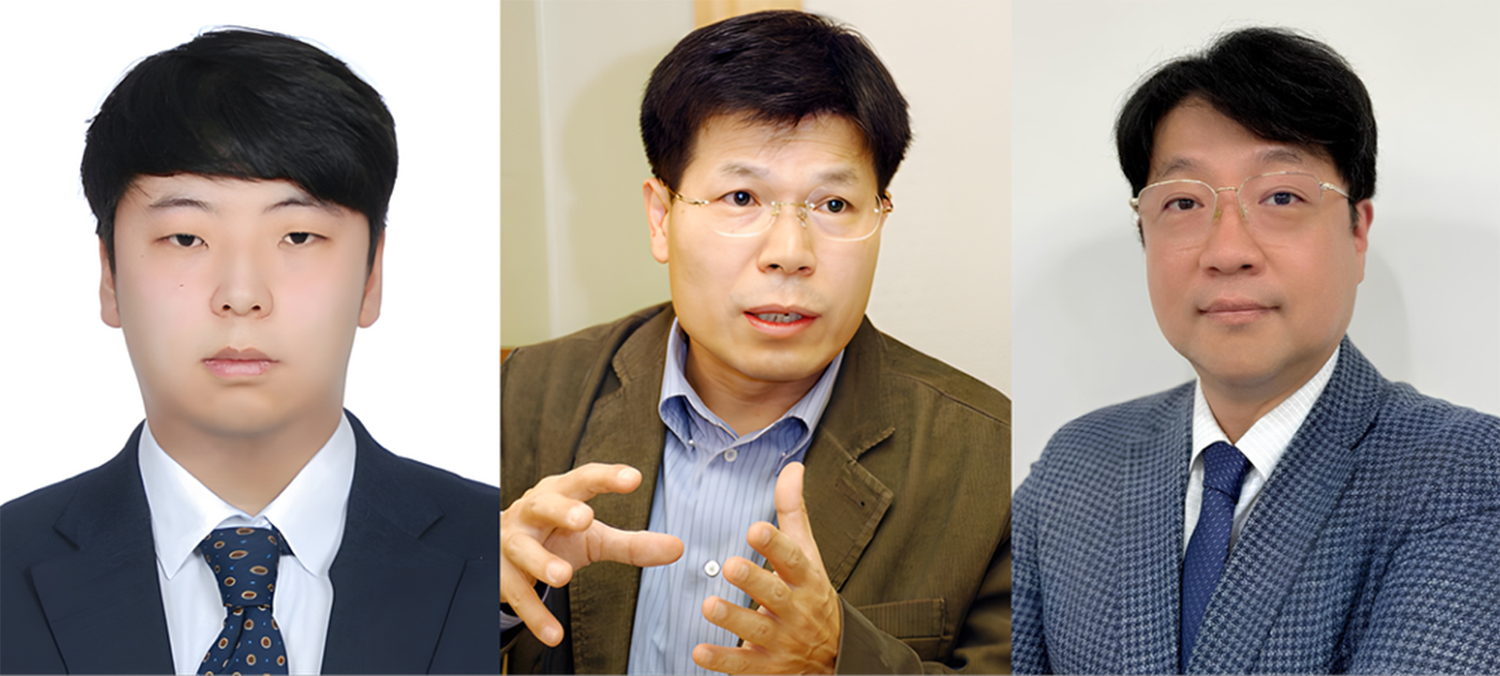

△ 왼쪽부터 김병국 박사수료생, 임권택 명예교수, 박상혁 교수.
국립부경대학교(총장 배상훈) 연구팀이 암세포에 대한 항암제 전달 효율을 향상시키는 ‘스마트 약물 전달 시스템’을 개발했다.
국립부경대 김병국 박사수료생(4차산업융합바이오닉스공학과)이 제1 저자, 임권택 명예교수와 박상혁 교수(의공학전공)가 교신저자로 참여한 연구팀이 개발한 ‘산화-환원반응 가교 말토헵타오스 기반 마이셀’이 그것.
이 시스템은 항암제인 독소루비신(Doxorubicin)의 비특이적 전달에 따른 낮은 항암 효율의 한계를 극복하기 위해 개발됐다. 독소루비신은 다양한 암 치료에 사용되는 매우 효과적인 항암제이지만, 여러 부작용을 초래하는 한계가 있다.
국립부경대 연구팀이 이번에 개발한 시스템은 생체적합성 올리고당인 말토헵타오스 기반의 A2B 믹토암 블록 공중합체로 구성되어 있고, 내부에 이황화결합(disulfide) 또는 이셀레나이드결합(diselenide) 가교를 이용해 체내 정상조직에는 영향을 주지 않으면서 암세포에 도달했을 때만 선택적으로 약물을 방출할 수 있도록 설계됐다.
연구팀의 실험 결과 이 시스템은 높은 약물 적재 효율을 보였고, 정상 세포와는 생체적합성을, 암세포에는 강력한 항암 효과를 보이는 것으로 나타났다.
박상혁 교수는 “이번 연구는 기존 약물 전달 시스템의 문제였던 혈액 내 조기 누출과 그로 인한 다양한 부작용 문제를 극복할 수 있는 새로운 방법을 밝힌 의의가 있다. 향후 항암제 정밀 투여 시스템이나 부작용 감소형 나노 약물 전달 플랫폼 등에 활용될 수 있어 학계와 산업계의 높은 관심이 기대된다.”라고 밝혔다.
이번 연구 결과를 담은 논문 ‘Redox-responsive core-cross-linked micelles of miktoarm maltoheptaose-b-poly(furfuryl methacrylate) for enhanced anticancer drug delivery’는 화학·재료공학 분야의 세계적인 국제학술지 <Carbohydrate Polymers>(JCR 상위 0.9%)에 최근 게재됐다. <부경투데이>
Pukyong National University Develops ‘Smart Drug Delivery System’ to Enhance Anticancer Drug Delivery to Tumor Cells
-Research team led by Ph.D. candidate Byeong Kook Kim, Professor Kwon Taek Lim, and Professor Sang-Hyug Park
-Developed redox-responsive maltopheptaose-based micelles; research published in international journal
A research team from Pukyong National University (President Bae Sang-hoon) has developed a “smart drug delivery system” that enhances the efficiency of anticancer drug delivery to tumor cells.
The system, titled “redox-responsive crosslinked maltopheptaose-based micelles,” was developed by Ph.D. candidate Byeong Kook Kim (Department of Industry 4.0 Convergence Bionics Engineering) as the first author, with Professor Kwon Taek Lim (Professor Emeritus) and Professor Sang-Hyug Park (Major of Biomedical Engineering, Division of Smart Healthcare) as corresponding authors.
The system was developed to overcome the limitations of low anticancer efficacy caused by the nonspecific delivery of doxorubicin, a potent anticancer drug widely used in the treatment of various cancers but known to cause several side effects.
The system developed by the Pukyong National University research team is composed of an A2B-type miktoarm block copolymer based on maltopentaose, a biocompatible oligosaccharide. It incorporates disulfide or diselenide crosslinking within the micelle core, enabling selective drug release only upon reaching cancer cells, while minimizing effects on healthy tissues.
Experimental results showed that the system exhibited high drug-loading efficiency, demonstrating biocompatibility with normal cells and strong anticancer effects against cancer cells.
Professor Sang-Hyug Park stated, “This study is significant in that it presents a novel method to overcome the early leakage of drugs into the bloodstream―a major issue in conventional drug delivery systems, which often leads to various side effects. The system holds promise for applications in precision anticancer drug delivery and reduced-side-effect nanomedicine platforms, garnering considerable interest from both academia and industry.”
The findings of this study were recently published in the prestigious international journal <Carbohydrate Polymers> (JCR Top 0.9%) in the field of chemistry and materials engineering, under the title ‘Redox-responsive core-cross-linked micelles of miktoarm maltoheptaose-b-poly(furfuryl methacrylate) for enhanced anticancer drug delivery.’ <Pukyong Today>